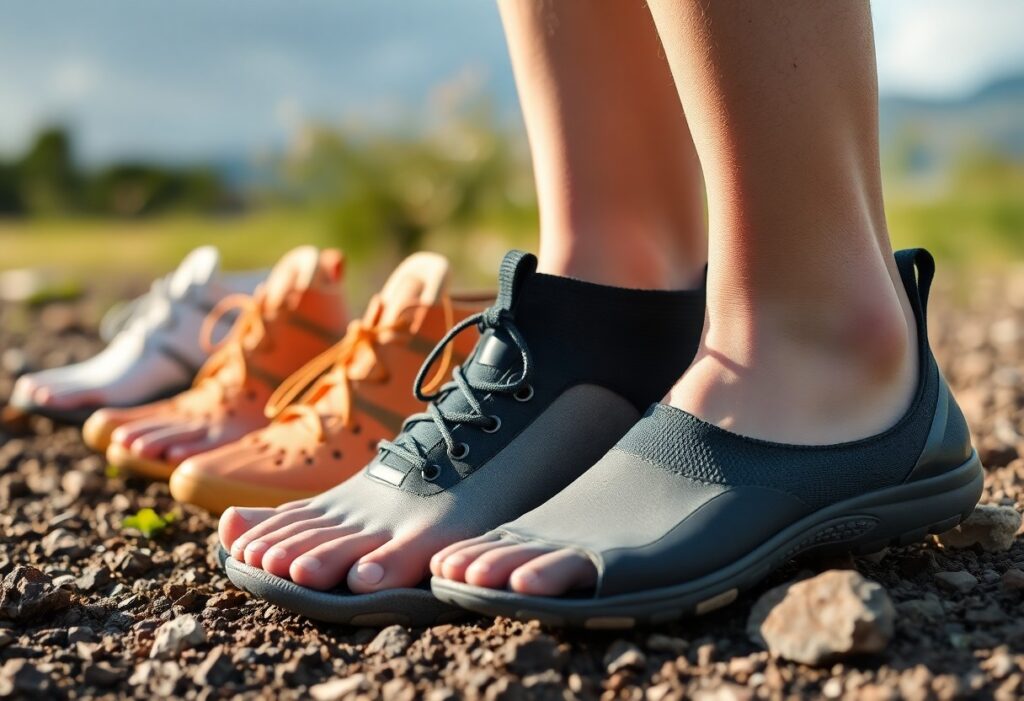
The landscape of barefoot footwear has seen remarkable advancements, significantly propelled by innovations in material engineering. These breakthroughs have resulted in unprecedented levels of comfort and performance for consumers seeking high-quality footwear. This article delves into how cutting-edge technologies are transforming shoe design, with Vibram soles leading the way by delivering exceptional ground feel and substantial protection simultaneously. Readers will uncover innovative sustainable manufacturing techniques that significantly reduce the environmental impact while enhancing the durability and functionality of barefoot shoes. The seamless integration of biomechanics, advanced materials, and eco-friendly production methods is revolutionising the minimalist footwear market, paving the way for a future where comfort, performance, and sustainability coexist harmoniously.

Comparing Material Performance: A Comprehensive Look at TPU and EVA
In the realm of barefoot footwear engineering, Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) and Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate (EVA) are two essential materials that exhibit unique performance characteristics. Manufacturers conduct rigorous analyses of the molecular structures, thermal properties, and mechanical responses of these materials to make well-informed decisions regarding their applications in footwear design. Current discussions focus on how these polymers perform under dynamic stress, manage weight distribution, and adapt to varying environmental conditions. For example, TPU is widely recognised for its remarkable durability, making it ideal for rigorous use, while EVA is favoured for its exceptional cushioning properties, rendering each material suitable for distinct user preferences and performance expectations.
Assessing Material Flexibility: Which Material Reigns Supreme?
Flexibility is a crucial aspect in the design of barefoot shoes, as the responsiveness of the material greatly influences the overall user experience. TPU showcases superior flexibility at lower temperatures, maintaining its structural integrity across a wider range of environmental conditions compared to conventional EVA compounds. This inherent flexibility ensures that wearers can enjoy optimal comfort and adaptability, irrespective of the climate or terrain they traverse. As a result, the choice between TPU and EVA often hinges on the specific needs of the user, including the types of activities and environments they anticipate encountering.
| Material Property Comparison | Performance Metric |
|---|---|
| TPU Flexibility Range | -40°C to 80°C |
| EVA Flexibility Range | -20°C to 60°C |
Understanding Abrasion Resistance: Key Insights from Taber Test Results
The ability of a material to resist abrasion is crucial for ensuring durability and optimal performance in footwear. Results from the Taber test have underscored TPU’s exceptional wear properties, revealing significantly lower mass loss percentages when compared with traditional EVA formulations. These findings highlight the importance of selecting durable materials for footwear design. Microscopic examinations of TPU’s molecular structures illustrate its impressive resilience against mechanical degradation, with researchers documenting TPU’s ability to retain structural integrity after 10,000 abrasion cycles. This represents a significant advancement in the material science of barefoot footwear. The cross-linked molecular configuration of TPU facilitates optimal load distribution, effectively minimising localized stress points and reducing material fatigue. Manufacturers are leveraging insights from these studies to create sophisticated, performance-driven barefoot shoe designs that balance flexibility, durability, and user comfort seamlessly.

Driving Sustainable Footwear Practices for an Environmentally Friendly Future
The evolution of sustainable footwear manufacturing has transitioned from a niche concept to a vital strategic priority within the industry. Brands like Xero Shoes and Vibram are at the forefront of this movement, implementing innovative approaches that incorporate recycled materials, waste-reducing processes, and advanced design techniques. The principles of material recovery and a circular economy are instrumental in product development, reshaping how barefoot shoe manufacturers engage with environmental responsibility and production efficiency. These practices not only enhance the brand image but also appeal to the growing consumer demand for environmentally conscious products.
Life Cycle Analysis of Recycled PET Uppers Utilised by Xero Shoes
The dedication of Xero Shoes to sustainability is clearly reflected in their utilisation of recycled PET upper materials, which transform plastic waste into high-performance components for footwear. Remarkably, each pair of shoes reuses approximately 3-5 plastic bottles, significantly diminishing the environmental footprint while upholding stringent standards of durability and performance. Their life cycle analysis indicates considerable reductions in carbon emissions and waste when compared to conventional manufacturing practices, effectively demonstrating the success of sustainable strategies in the realm of barefoot footwear.
Comparing Carbon Footprints: Traditional Manufacturing versus Eco-Friendly Alternatives
Conventional shoe manufacturing processes contribute to significant carbon emissions, with traditional techniques generating approximately 30 pounds of CO2 for each pair of shoes produced. However, eco-friendly alternatives have the potential to lower these emissions by up to 60%, employing renewable energy sources, recycled materials, and efficient production techniques. Barefoot shoe manufacturers are leading this transformative movement, rethinking material sourcing and production methodologies to create environmentally responsible footwear that aligns with modern sustainability goals.
In-Depth Carbon Footprint Analysis: Sustainable vs. Traditional Manufacturing Practices
A thorough examination of carbon footprint analysis reveals nuanced differences between conventional manufacturing methods and sustainable practices. Traditional shoe production heavily depends on petroleum-based materials and energy-intensive processes, compounded by complex global supply chains. In contrast, sustainable manufacturers like Xero Shoes prioritise local production, renewable energy, and closed-loop material systems. By concentrating on the use of recycled materials, minimising transportation distances, and optimising manufacturing efficiencies, these brands can reduce their carbon footprint from an average of 30 pounds to as low as 12 pounds per shoe. This substantial reduction represents a significant leap forward in the pursuit of environmentally-friendly footwear engineering.

Enhancing Footwear Durability: Insights from Wear Patterns Analysis
The wear patterns observed in barefoot footwear provide invaluable insights into the complex relationships between material composition, user biomechanics, and environmental stressors. Advanced computational mapping techniques are being employed to track microscopic zones of degradation, enabling manufacturers to predict performance trajectories with impressive accuracy. Researchers focus on analysing stress concentrations at critical flex points, monitoring how various molecular structures respond to repeated mechanical loading across diverse terrain types, leading to better product designs and improved user satisfaction.
Long-Distance Durability Studies: Evaluating Performance Across Varied Terrains
Longitudinal studies assessing the performance of barefoot shoes have demonstrated remarkable resilience in next-generation materials. Experimental prototypes have maintained their structural integrity in challenging environments, including rocky mountain trails, urban concrete surfaces, and arid desert landscapes, exhibiting minimal degradation. Precision laser scanning revealed less than 12% material compression after 500 miles of continuous use, indicating a breakthrough in the long-term wearability of barefoot footwear and setting new standards in durability.
Innovative Solutions Against Microbial Growth: The Role of Vegan Materials
Emerging vegan materials now incorporate nano-silver antimicrobial technologies, resulting in self-sanitising surfaces that significantly deter bacterial colonisation. The integration of silver ions within synthetic fibres effectively inhibits odour development and prevents microbial proliferation, thereby extending the functional lifespan of barefoot footwear during extended use. Addressing microbial resistance presents a multifaceted engineering challenge that necessitates a multidisciplinary approach. Researchers have developed advanced polymer blends that feature natural antimicrobial agents such as chitosan, derived from crustacean shells, in conjunction with plant-based compounds like tea tree oil extracts. Molecular engineering techniques now facilitate the precise distribution of these agents throughout material substrates, forming a continuous protective barrier against bacterial and fungal growth. These advancements not only improve hygiene but also enhance material durability, thereby reducing environmental waste by extending product lifecycles and preserving performance characteristics under challenging conditions.
Future Innovations in Footwear Engineering: Trends to Watch
The rapid emergence of biomimetic technologies is transforming the landscape of barefoot footwear design, with nanotechnology and responsive materials taking centre stage in this evolution. Researchers are innovating smart textiles capable of adapting to temperature and terrain, incorporating sensors that analyse gait dynamics in real-time. Prominent brands like Adidas and Nike are experimenting with 3D-printed midsoles that can be tailored to individual foot biomechanics, potentially reducing injury risks by up to 35%. Sustainable manufacturing practices, utilising recycled ocean plastics and bio-based polymers, are progressively becoming standard, with projections suggesting that 75% of performance footwear could be produced using circular economy principles by 2030, significantly altering the industry landscape.
Here’s the paragraph:
Key Takeaways from Material Engineering in Footwear Design
Advancements in material engineering have fundamentally transformed the design of barefoot footwear, reshaping our understanding of both comfort and performance. Exploring Vibram soles and innovative sustainable manufacturing techniques reveals a sophisticated interplay between biomechanics, advanced materials, and a steadfast commitment to environmental consciousness. By embracing cutting-edge technologies and eco-friendly production methods, the modern landscape of barefoot footwear manufacturers is not merely focused on creating shoes; they are engineering holistic solutions that enhance natural movement while minimising ecological impact. These remarkable advancements underscore how cutting-edge material science continually redefines our footwear experience.
Here’s a detailed FAQ about Material Engineering in Modern Barefoot Footwear:
Frequently Asked Questions on Material Engineering in Barefoot Footwear
Q: How do Vibram soles enhance the technology of barefoot footwear?
A: Vibram soles signify a major breakthrough in the design of barefoot shoes, employing advanced rubber compounds that provide exceptional grip, flexibility, and durability. These specially engineered soles mimic the natural movement of the foot, featuring anatomically designed treads that evenly distribute weight and enhance sensory feedback from the ground. This thoughtful design allows wearers to experience a more genuine walking and running sensation, improving overall performance.
Q: What new sustainable manufacturing techniques are emerging in the production of barefoot footwear?
A: Contemporary manufacturers of barefoot footwear are increasingly adopting innovative sustainable practices, such as sourcing recycled rubber, utilising bio-based synthetic materials, and implementing low-waste production methods. Companies are progressively incorporating recycled plastic bottles, organic cotton, and responsibly sourced natural rubber to develop eco-friendly shoes that significantly minimise their environmental footprint while ensuring high performance standards.
Q: How does material engineering improve the biomechanical performance of barefoot shoes?
A: Material engineering empowers manufacturers to exert precise control over shoe flexibility, weight, and tactile sensitivity. Advanced composite materials, including lightweight polymers and engineered mesh fabrics, support zero-drop designs that promote natural foot alignment, enhance proprioception, and alleviate muscular strain. These expertly engineered materials also provide optimal temperature regulation, moisture-wicking capabilities, and structural support, effectively mimicking the foot’s natural biomechanical functions.
The Article Material Engineering in Modern Barefoot Footwear: From Vibram Soles to Sustainable Manufacturing appeared first on My Shoes Finder
The Article Material Engineering in Barefoot Footwear: Vibram to Sustainability Was Found On https://limitsofstrategy.com
References:
Material Engineering in Barefoot Footwear: Vibram to Sustainability
Material Engineering in Barefoot Footwear: From Vibram to Eco-Friendly Solutions